An Editorial on Hackerrank gave a really nice review of certain number theory concepts:-
Namely
Lucas' theorem



Namely
- Lucas' Theorem to determine
.gif) modulo p where p is prime.
modulo p where p is prime. - Chineese remainder theoram to find x modulo (a1.a2) where x modulo(a1) and x modulo(a2) are given.
- Extended Euclidean algorithm to find pair of integers c1,c2 such that.
So remaining posts will be about these concepts only.
Lucas' theorem

Where


Images taken from :- Lucas Theorem Wikipedia
But these images don't provide much of an explaination as such, (at least when I read them)
The approach of Lucas' thoram can be summarized by a simple procedure In the following manner. To find the 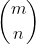 modulp p where p is a prime
modulp p where p is a prime
- Express m in the base p
- Express n in the base p
- Incase the expansion of n contains less number of digits than m, pad leading zeroes to the left of the expansion of n
- Take digitwise combination of each pair of digits.
- Multiply the obtained terms to find the value of desired combination and take modulo p.
Now will be building our number theory library so hence I will be posting the codes for the above mentioned theorams:-
Python :-
Python :-
- from math import factorial
- f=factorial
- def ncr(a,b):
- if b>a:
- return 0
- return f(a)/(f(a-b)*f(b))
- def conv(a,b):
- s=[]
- while a:
- s.append(a%b)
- a=a//b
- return s[::-1]
- def main():
- n,m,p=map(int,raw_input().split()) #input m , n and the prime
- k1=conv(n,p) #convert to base p
- k2=conv(m,p)
- if len(k2) < len(k1):
- k2= [0]*(len(k1)-len(k2))+k2 #pad in leading zeroes
- l=[]
- for i in xrange(len(k1)):
- l.append(ncr(k1[i],k2[i])) #take digitwise ncr
- prod=1
- for i in l:
- prod*=i
- prod%=p
- print prod
- main()
No comments:
Post a Comment